In this article, you will gain a clear understanding of pyramid schemes, their definition, and how they operate. Pyramid schemes are a type of fraudulent business model that entices individuals with the promise of high profits and financial success. However, underneath their alluring veneer lies a scheme that primarily relies on recruiting new members to sustain its operation. By exploring the characteristics and mechanics of pyramid schemes, you will be equipped with the knowledge to protect yourself and others from falling victim to these deceptive practices. So, let’s unravel the truth behind pyramid schemes and empower ourselves with valuable information.
Definition of a Pyramid Scheme
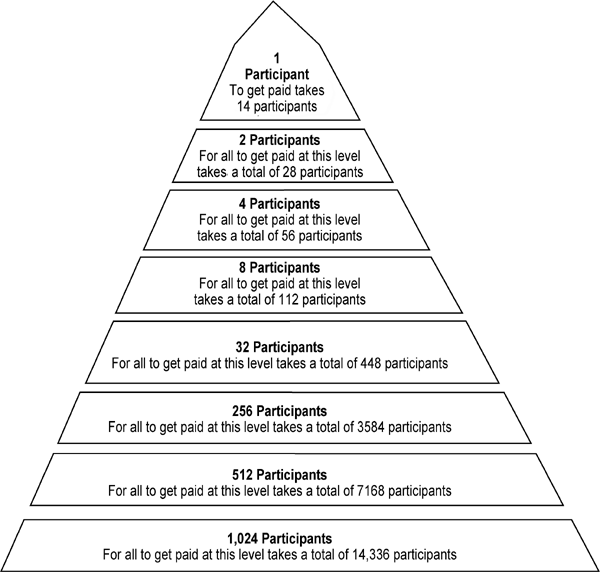
A pyramid scheme is a fraudulent business model that relies on recruiting members rather than selling actual products or services. In this scheme, participants are promised high profits for simply recruiting others to join the scheme. The underlying structure resembles a pyramid, with a limited number of people at the top earning the majority of the profits, while those at the bottom are left with little to no return on their investment.
History of Pyramid Schemes
The concept of pyramid schemes can be traced back centuries, with some even suggesting that they originated in ancient civilizations. However, the term “pyramid scheme” itself gained popularity in the 20th century. It was during this time that various notorious schemes made headlines, causing governments and regulators to take action.
Characteristics of Pyramid Schemes
Pyramid schemes share several common characteristics that help distinguish them from legitimate multi-level marketing (MLM) or direct selling companies. These characteristics include:
High Emphasis on Recruiting
One of the key characteristics of a pyramid scheme is the heavy focus on recruiting new members. Participants are often required to recruit a certain number of individuals who, in turn, recruit others. The emphasis on recruitment is prioritized over actual product sales.
Promise of Easy Money
Pyramid schemes lure participants with the promise of quick and substantial profits. They appeal to individuals seeking financial success without significant effort or skill. The promoters often use catchy slogans or testimonials to convince potential recruits that they can achieve financial freedom by joining the scheme.
Lack of Tangible Products or Services
Unlike legitimate MLM companies, pyramid schemes usually lack genuine products or services. While they may claim to have products, in reality, these are often low-quality or overpriced items with little demand. The main focus remains on recruiting new members rather than selling legitimate products or services.
Unsustainable Financial Structure
Pyramid schemes rely on an unsustainable financial structure that ultimately leads to the majority of participants losing their money. As the pyramid grows, it becomes increasingly difficult to recruit new members, resulting in a collapse of the scheme. Only a small percentage of participants at the top of the pyramid profit at the expense of the majority at the bottom.
How Pyramid Schemes Work
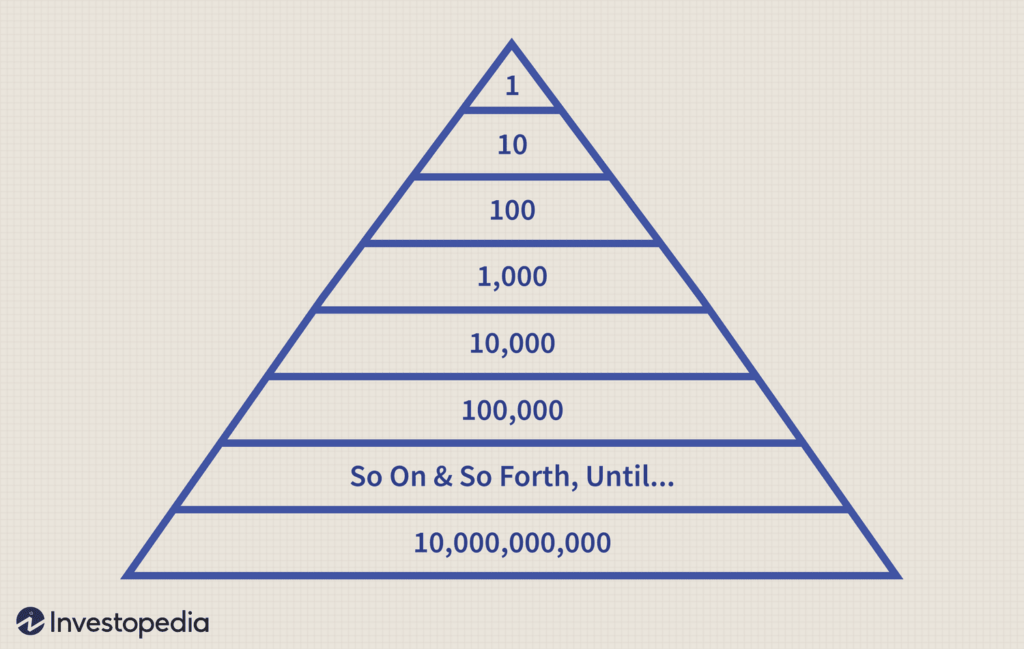
Pyramid schemes operate by promising participants high returns for recruiting others. They typically follow a step-by-step process that manipulates individuals into believing they are participating in a legitimate business venture. Although the exact methods may vary, the general workings of a pyramid scheme can be described as follows:
-
Initial Investment: Participants are required to pay an initial fee or buy into the scheme with a certain amount of money. This may be disguised as a membership fee, product purchase, or investment.
-
Recruitment: Participants are encouraged to recruit others into the scheme. They are promised a portion of the recruits’ investments or payments as their own profits.
-
Revenue Generation: As new members join, their investments are used to pay off the earlier participants, creating a false sense of profitability. The early recruits receive some return on their investment, which further entices them to promote the scheme.
-
Pyramid Growth: The pyramid continues to grow as more individuals are recruited, with each tier relying on the recruitment of new members to sustain the scheme.
-
Collapse: Eventually, the scheme becomes unsustainable, as recruitment slows down or comes to a halt. When the pyramid collapses, the majority of participants, particularly those at the bottom, are left with losses, while only a few individuals at the top benefit from the proceeds.

Different Types of Pyramid Schemes
While the basic structure of all pyramid schemes is the same, there are different variations that have emerged over time. These variations may employ different tactics or target specific groups of individuals. Some of the common types of pyramid schemes include:
Ponzi Schemes
Ponzi schemes are a type of pyramid scheme named after Charles Ponzi, who gained notoriety for his fraudulent activities in the early 20th century. In a Ponzi scheme, the operator uses funds from new investors to pay returns to earlier investors, giving the impression of legitimate profits. However, in reality, there is no genuine investment activity, and the scheme eventually collapses when there is not enough new money to sustain it.
Matrix Schemes
Matrix schemes involve a matrix-like structure where participants are organized into several levels or matrices. Each level requires a certain number of recruits before moving to the next level, with the promise of increasing profits at each stage. Matrix schemes often promote products or services of low value, with the primary focus on recruiting new members.
Gifting Schemes
Gifting schemes operate by claiming to be a form of charity or philanthropy, where participants exchange money or gifts with the expectation of receiving more in return. These schemes often disguise themselves as legal gifting practices but ultimately rely on the recruitment of new participants. The exchange of money or gifts is not based on the value of the items but rather on the ability to recruit others into the scheme.
Examples of Infamous Pyramid Schemes
Over the years, several pyramid schemes have gained notoriety due to the significant financial losses suffered by participants. Some well-known pyramid schemes include:
Bernie Madoff’s Ponzi Scheme
Bernie Madoff’s Ponzi scheme is perhaps one of the most infamous and largest financial frauds in history. Madoff operated a massive Ponzi scheme that defrauded thousands of investors out of billions of dollars. Madoff promised steady returns to his clients, using new investments to pay off earlier investors. The scheme eventually collapsed in December 2008, leading to Madoff’s arrest and subsequent imprisonment.
ACN Inc.
ACN Inc., a multi-level marketing company, faced allegations of operating as a pyramid scheme in the early 2000s. While ACN claimed to offer telecommunication services, critics argued that the real profits came from recruitment rather than product sales. The company faced lawsuits and regulatory scrutiny over its business practices, but ultimately settled the charges without admitting any wrongdoing.
Zeek Rewards
Zeek Rewards was an online penny auction and revenue-sharing program that operated as a pyramid scheme. Participants bought bids and recruited others to invest in the program, with promised returns on their investments. However, the majority of the revenue came from the recruitment of new participants, resulting in substantial financial losses for those at the bottom of the pyramid. In 2012, the United States Securities and Exchange Commission shut down Zeek Rewards, labeling it a $600 million Ponzi scheme.

Warning Signs of a Pyramid Scheme
Recognizing the signs of a pyramid scheme is crucial to protect yourself and others from falling victim to these fraudulent schemes. Some warning signs to watch out for include:
Emphasis on Recruitment
Pyramid schemes often prioritize recruitment over actual product sales. If the focus is primarily on recruiting new members, with little emphasis on selling genuine products or services, it may be a red flag indicating a pyramid scheme.
Promise of High Returns with Little Effort
Be wary of schemes that promise exorbitant profits with minimal effort or skills required. Legitimate businesses typically do not offer easy money without actual work or value creation.
Lack of Legitimate Products or Services
Pyramid schemes may claim to have products or services, but often these are of low quality, overpriced, or of little demand. Take a close look at what is being offered and assess if there is genuine value beyond the recruitment aspect.
Complicated Compensation Structure
If the compensation plan of a business opportunity is overly complex or difficult to understand, it could be a sign of a pyramid scheme. Legitimate MLM companies have transparent compensation plans that are based on product sales rather than the recruitment of new members.
Legal Status and Consequences
Pyramid schemes are illegal in most countries, including the United States. Participating in or promoting a pyramid scheme can have severe legal consequences. Individuals involved in pyramid schemes may face charges such as fraud, conspiracy, and money laundering. Authorities regularly crack down on these schemes, shutting them down and prosecuting those responsible for orchestrating them.
Effects of Pyramid Schemes
The effects of pyramid schemes can be devastating, both financially and emotionally, for the victims involved. Those who invest in pyramid schemes often experience significant financial losses, sometimes losing their life savings in the process. These losses can lead to financial ruin, strained relationships, and even bankruptcy. Additionally, the emotional impact can be severe, as individuals may feel betrayed, embarrassed, or deceived.
Alternative Business Models
Legitimate multi-level marketing (MLM) or direct selling companies offer an alternative to pyramid schemes. These businesses focus on selling genuine products or services while providing participants with the opportunity to earn a commission from the sales they generate. Unlike pyramid schemes, MLM companies have transparent compensation plans and place emphasis on product sales rather than the recruitment aspect. It is important to research and evaluate any business opportunity before getting involved, ensuring that it aligns with legal and ethical practices.
In conclusion, pyramid schemes are deceptive business models that rely on the recruitment of participants rather than legitimate product sales. Recognizing the warning signs and understanding the characteristics of pyramid schemes is essential to protect oneself from the financial and emotional consequences associated with these fraudulent schemes. By promoting awareness and fostering a culture of skepticism, individuals can safeguard themselves and others from falling prey to pyramid schemes, while exploring legitimate business opportunities that offer a sustainable path to financial success.