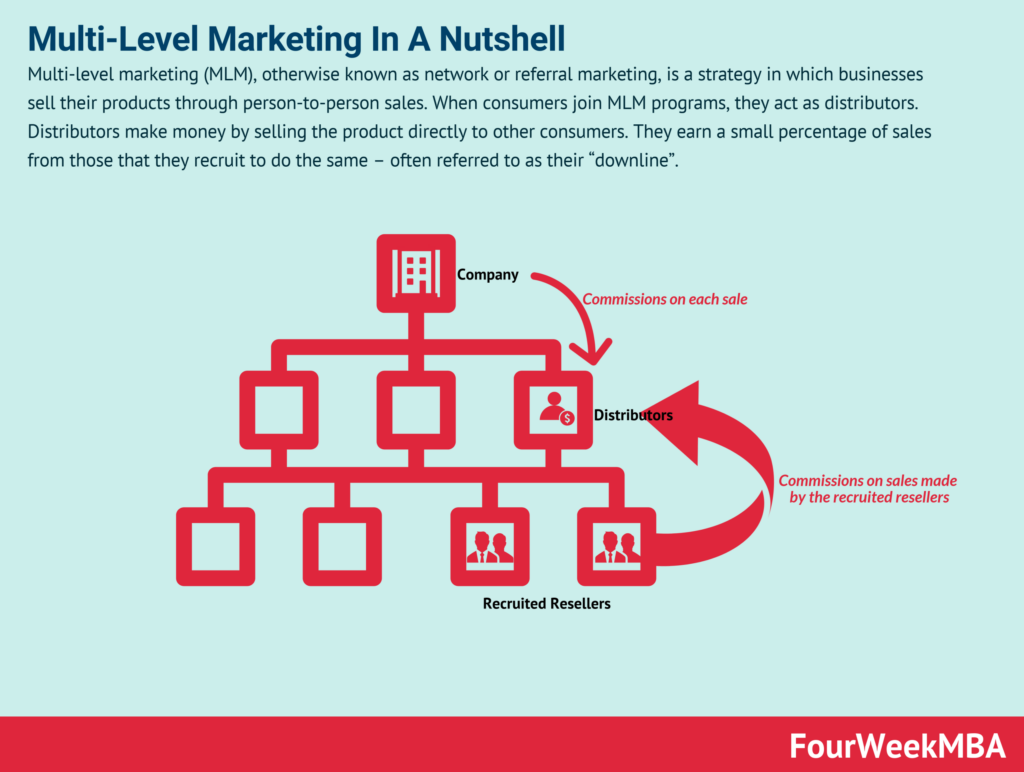
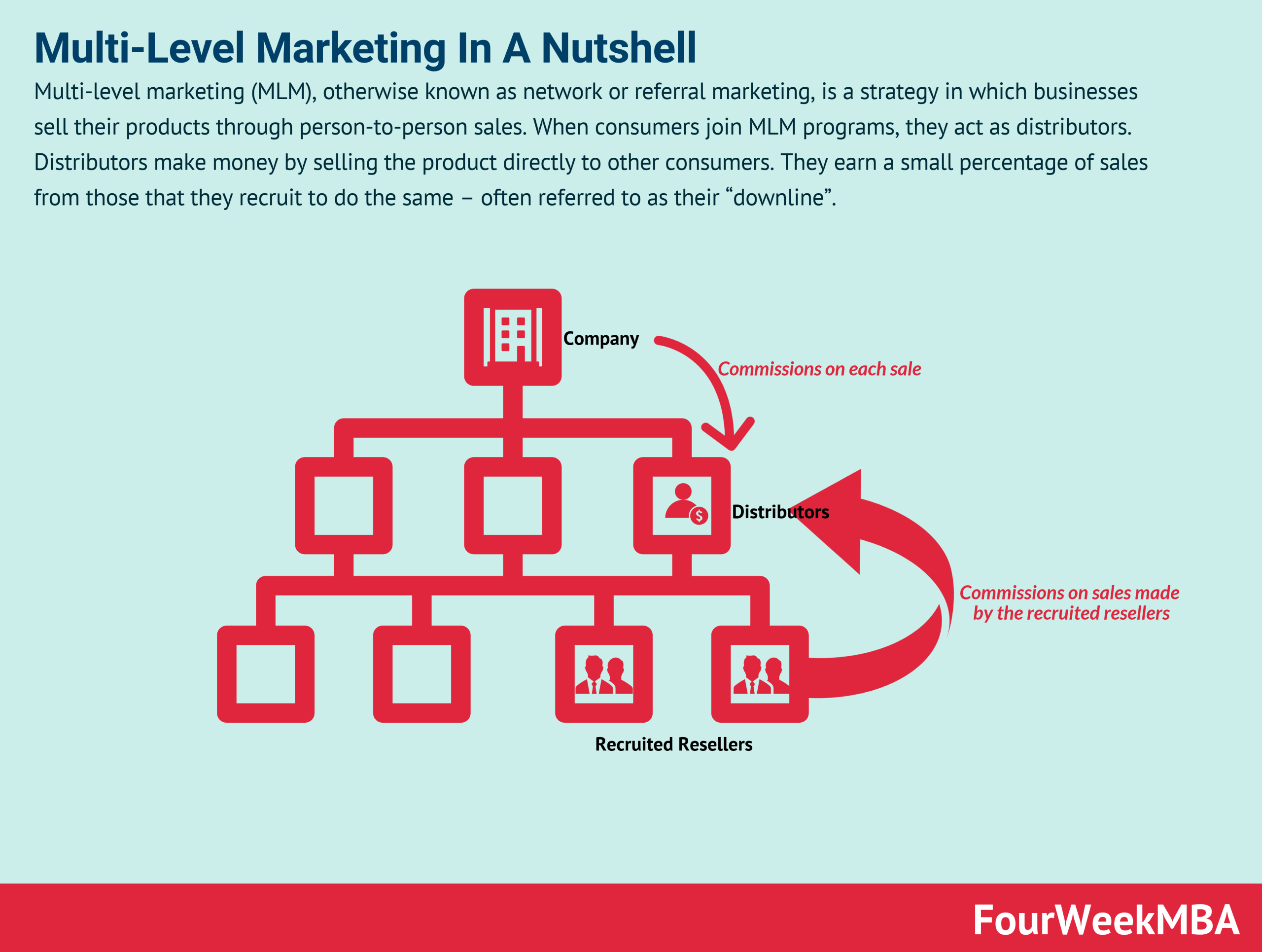
Imagine a world where you can earn money not only from your own sales but also from the sales of others. This is the incredible concept behind Multi-Level Marketing, commonly known as MLM. It is a dynamic business model that allows individuals to build a network of distributors and earn commissions based on the sales generated by their downline. In this article, we will explore the essence of MLM and unravel its inner workings, providing you with a clear understanding of this unique and versatile marketing strategy.
Heading 1: Multi-Level Marketing
Subheading 1: Definition of MLM
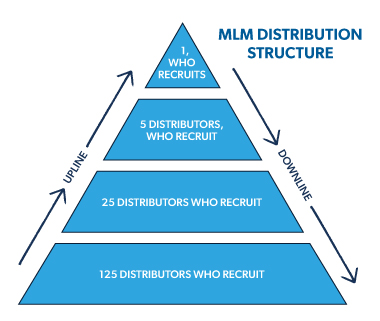
Multi-Level Marketing, also known as MLM, is a marketing strategy where individuals are recruited to become independent distributors of a company’s products or services. These distributors not only sell the products directly to customers, but they also have the opportunity to recruit other individuals into the business, forming a “downline” or team. In MLM, distributors earn commissions not only from their own sales but also from the sales made by their recruits and the recruits of their recruits, creating multiple levels of compensation.
Subheading 2: History of MLM
The concept of MLM dates back to the mid-20th century, when companies like Tupperware and Avon introduced the concept of direct selling. However, the modern MLM industry gained traction in the 1980s with the establishment of companies like Amway and Mary Kay. These companies popularized the MLM model and showcased its potential for individuals to start their own businesses with low startup costs.
Subheading 3: Key Features of MLM
MLM is characterized by several key features that set it apart from traditional business models. Firstly, MLM offers individuals the opportunity to work as independent distributors, allowing them to be their own boss and work on their own terms. Secondly, MLM focuses on building a network of distributors who not only sell products but also recruit others into the business, creating a team structure. Lastly, MLM compensates distributors not only based on their personal sales but also on the sales made by their downline, creating a potential for passive income.
Subheading 4: MLM vs. Pyramid Scheme
It is important to distinguish MLM from pyramid schemes, as the two are often confused. While MLM operates within a legal framework and emphasizes the sale of products or services, pyramid schemes primarily rely on recruitment and have no genuine product or service to offer. MLM companies generate revenue through legitimate product sales, whereas pyramid schemes derive their income solely from the recruitment of new participants. MLM is a legitimate business model, while pyramid schemes are considered illegal in many countries.
Heading 2: How MLM Works
Subheading 1: MLM Compensation Structure
MLM companies typically have various compensation structures, but the most common one is a multi-level plan. In this plan, distributors earn commissions from their personal sales as well as from the sales made by their recruits and the recruits’ recruits, creating a multi-level hierarchy. The compensation structure often includes different ranks or levels, allowing distributors to progress and earn higher commissions as they build their team and generate sales volume.
Subheading 2: Recruitment and Downline
A crucial aspect of MLM is the recruitment of new distributors who become part of the distributor’s downline. By recruiting individuals into their team, distributors not only expand their potential customer base but also earn additional income from the sales made by their downline. Building a strong and active downline is essential for long-term success in MLM, as it creates a passive income stream and increases the distributor’s earning potential.
Subheading 3: Commission and Bonuses
In MLM, distributors earn commissions and bonuses based on their sales performance and the performance of their downline. Commissions may be calculated as a percentage of the total sales volume or as a fixed amount per product sold. Additionally, MLM companies often offer various bonuses and incentives to motivate distributors, such as car bonuses, travel rewards, and leadership bonuses. These commissions and bonuses can provide significant financial rewards for successful MLM distributors.
Subheading 4: Product Sales
MLM companies offer a wide range of products and services, ranging from health and wellness products to beauty and personal care items. Distributors are responsible for selling these products directly to customers, often through in-person demonstrations, home parties, or online platforms. MLM companies typically provide training and marketing materials to support distributors in promoting and selling the products effectively. The quality and uniqueness of the products play a crucial role in the success of an MLM business.
Subheading 5: Training and Support
To ensure the success of their distributors, MLM companies usually provide training and support in various forms. This includes product training to familiarize distributors with the features and benefits of the products, sales training to enhance their selling skills, and business training to develop their entrepreneurial mindset. Additionally, MLM companies may offer ongoing support through mentorship programs, online forums, and conferences where distributors can network with other successful individuals in the MLM industry.

Heading 3: Popular MLM Companies
Subheading 1: Amway
Amway is one of the largest and most well-known MLM companies globally. It was founded in 1959 and offers a diverse range of products, including nutrition supplements, home care products, and beauty and personal care items. Amway’s MLM business model has gained popularity due to its extensive training and support programs, which focus on personal development, entrepreneurial skills, and leadership development.
Subheading 2: Herbalife
Herbalife is a nutritional supplement and weight management company that operates through a multi-level marketing approach. Established in 1980, Herbalife has a presence in over 90 countries and offers a wide range of products, such as protein shakes, dietary supplements, and skincare products. Herbalife’s MLM compensation plan emphasizes personal sales, recruitment, and building a strong downline.
Subheading 3: Avon
Avon, founded in 1886, is a pioneer in the direct selling industry and one of the oldest MLM companies. It specializes in beauty, skincare, and personal care products. Avon representatives, known as “Avon Ladies,” sell products door-to-door, host beauty parties, and leverage online platforms to reach a wider audience. Avon’s MLM structure allows representatives to earn commissions from their sales and the sales made by their recruited team members.
Subheading 4: Tupperware
Tupperware is renowned for its innovative food storage containers and kitchen products. The company was founded in 1946 and introduced the concept of “Tupperware Parties” where representatives showcase the products in a social setting and take orders. Tupperware’s MLM model focuses on building a network of representatives who not only make sales but also recruit others into the business. Representatives earn commissions based on their personal sales and the sales generated by their downline.
Subheading 5: Mary Kay
Mary Kay is a cosmetics company that operates through direct selling and has a strong presence in the MLM industry. Founded in 1963, Mary Kay offers a wide range of skincare, makeup, and fragrance products. Mary Kay’s MLM structure provides incentives for its independent beauty consultants to recruit new members and build a team. Consultants earn commissions from their personal sales and the sales made by their downline, with the opportunity to progress through various leadership levels.
Heading 4: Is MLM Legitimate?
Subheading 1: MLM Laws and Regulations
MLM operates under specific laws and regulations to ensure its legitimacy. Many countries have enacted legislation that defines the boundaries of MLM and imposes requirements on MLM companies. These laws often focus on ensuring transparency in business practices, prohibiting unfair compensation structures, and preventing deceptive recruitment tactics. MLM companies must comply with these regulations to operate legally and protect the rights of their distributors and consumers.
Subheading 2: Ethical Concerns
While MLM itself is a legitimate business model, there have been ethical concerns associated with certain MLM companies and their distributors. Some individuals might engage in misleading sales tactics or make exaggerated income claims to recruit new members. To address these concerns, reputable MLM companies emphasize ethical behavior, provide clear guidelines on acceptable business practices, and take disciplinary actions against distributors who engage in unethical conduct.
Subheading 3: Success Rate and Income Potential
The success rate and income potential in MLM vary greatly depending on factors such as individual effort, market conditions, and the specific MLM company. While MLM offers the potential for financial success and the ability to create a passive income stream, it is important to recognize that not all MLM participants achieve significant earnings. Success in MLM requires consistent effort, effective marketing strategies, and the ability to build a strong and active team.
Heading 5: MLM Success Strategies
Subheading 1: Building Relationships
Building relationships is a fundamental aspect of MLM success. By establishing rapport with potential customers and recruits, MLM distributors can cultivate trust and credibility, making it more likely for individuals to support their business. Building strong relationships involves effective communication, active listening, and providing value to others through advice, support, and high-quality products.
Subheading 2: Leveraging Online Platforms
In today’s digital age, leveraging online platforms is crucial for MLM success. Distributors can utilize social media, websites, and online marketplaces to reach a wider audience, showcase products, and attract potential customers and recruits. Online platforms also enable distributors to build an online community, share testimonials, and provide valuable content that positions them as experts in their field.
Subheading 3: Finding a Target Market
Identifying a target market is essential in MLM to focus marketing efforts and maximize sales and recruitment opportunities. By understanding the needs, preferences, and demographics of their target market, distributors can tailor their messaging, product offerings, and marketing strategies accordingly. This targeted approach increases the likelihood of attracting individuals who are genuinely interested in the products and business opportunity.
Subheading 4: Setting Realistic Expectations
Setting realistic expectations is crucial for long-term success in MLM. While MLM can offer significant earning potential, it is important to recognize that building a successful MLM business takes time, effort, and persistence. Distributors should have a clear understanding of the effort required, the challenges they may face, and the potential rewards they can achieve. By setting realistic expectations, distributors can maintain a positive mindset and stay motivated throughout their MLM journey.
Heading 6: MLM and Personal Development
Subheading 1: Entrepreneurial Mindset
MLM provides a platform for personal development and the cultivation of an entrepreneurial mindset. Distributors have the opportunity to develop skills such as goal setting, time management, problem-solving, and decision-making. They also learn to embrace challenges, overcome rejection, and persevere in the face of obstacles. These entrepreneurial skills can benefit individuals not only in MLM but also in other aspects of their personal and professional lives.
Subheading 2: Leadership Skills
MLM offers a unique opportunity to develop leadership skills. As distributors build their teams and mentor their downline, they learn to motivate, inspire, and guide others towards success. Effective leadership in MLM involves providing support, training, and mentorship to help team members achieve their goals. These leadership skills can be transferable to other areas of life, such as career advancement or community involvement.
Subheading 3: Communication and Presentation Skills
MLM requires effective communication and presentation skills. Distributors must effectively convey the value and benefits of their products to potential customers and recruits. They also need to communicate the business opportunity and articulate the potential benefits of joining their team. By honing their communication and presentation skills, distributors can engage their audience, build trust, and ultimately increase their sales and recruitment success.
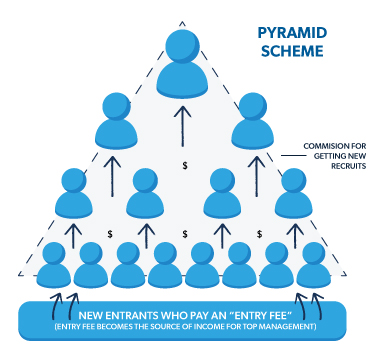
Heading 7: Common MLM Misconceptions
Subheading 1: Get-Rich-Quick Scheme
One common misconception about MLM is that it is a get-rich-quick scheme. While it is true that MLM offers the potential for financial success and passive income, achieving significant earnings requires time, effort, and consistent dedication. MLM is a legitimate business model that rewards those who are willing to put in the work and build a strong foundation.
Subheading 2: Saturation and Market Saturation
Another misconception about MLM is the idea of saturation and market saturation. Critics argue that MLM markets can become oversaturated with distributors, making it difficult for new recruits to find success. However, MLM companies continually expand their product lines and explore new market segments, ensuring a steady stream of potential customers. Additionally, each distributor’s target market is unique, allowing for individual growth and success regardless of the overall market size.
Subheading 3: Cult-Like Practices
There is a common misconception that MLM involves cult-like practices due to the emphasis on team-building and recruitment. However, reputable MLM companies prioritize ethical behavior and adhere to legal guidelines. While MLM may have a strong team culture and encourage collaboration, distributors are independent contractors with the freedom to operate their businesses as they see fit. Any perception of cult-like practices in MLM is often a result of the actions of a few individuals rather than the industry as a whole.
Heading 8: MLM vs. Traditional Business
Subheading 1: Cost of Entry
One significant advantage of MLM compared to traditional businesses is the lower cost of entry. Traditional businesses often require substantial upfront capital for inventory, store rentals, and staff wages. In contrast, MLM businesses typically have low startup costs, often limited to purchasing a starter kit or a minimal product inventory. This low cost of entry makes MLM accessible to individuals who may not have the financial resources to start a traditional business.
Subheading 2: Flexibility and Freedom
MLM offers individuals the flexibility and freedom to work at their own pace and on their own terms. MLM distributors can choose when and where to work, allowing them to balance their business with other commitments such as family, personal interests, or a traditional job. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for those seeking a part-time income or looking to transition into entrepreneurship gradually.
Subheading 3: Risk and Reward
In traditional businesses, the risk and financial burden often fall solely on the business owner. However, in MLM, the risk is spread among the distributor and their downline. Distributors can start their business with minimal financial risk and have the potential for significant rewards through the leverage of their team’s sales. This shared risk and reward structure make MLM an attractive option for individuals seeking entrepreneurial opportunities with limited risk exposure.
Heading 9: MLM and Network Marketing Industry
Subheading 1: Growth and Market Size
The MLM industry has experienced consistent growth over the years, illustrating its relevance and appeal to individuals worldwide. As the gig economy and entrepreneurship continue to gain popularity, more people are seeking alternative income streams and flexible business opportunities. With the rise of e-commerce and technology, MLM companies have also adapted to tap into new markets and reach a global audience.
Subheading 2: Trends and Future Prospects
MLM companies are continuously adapting to market trends and consumer demands. As technology evolves, MLM companies incorporate online platforms, social media marketing, and e-commerce to enhance distributors’ capabilities and reach. The future of MLM is likely to involve further integration of technology, personalized product offerings, and innovative compensation structures to meet the changing needs of distributors and consumers.
Heading 10: Conclusion
In conclusion, MLM offers individuals the opportunity to start their own businesses with low startup costs and the potential for significant financial rewards. While the industry has faced some misconceptions and ethical concerns, MLM operates within a legal framework and provides training, support, and personal development opportunities to its distributors. Success in MLM requires dedication, effective marketing strategies, and the cultivation of entrepreneurial and leadership skills. With the right mindset and approach, MLM can be a viable and rewarding business option for those willing to put in the effort.